Contrary to what manufacturers claim about refrigerants, our hands-on testing revealed that not all are created equal. I examined several options, from simple oil testers to advanced analyzers, and the one that stood out was the 6PCS AC Oil & Refrigerant Analyzer Kit for R134a/R1234yf. It’s compact, precise, and perfect for both DIYers and pros. This kit accurately detects low oil levels and harmful acids without draining the system, saving you time and preventing costly repairs.
What really caught my attention is how easy it is to use—just connect, press, and get instant readings—plus the reusable design adds long-term value. It outperforms basic testers by offering a comprehensive analysis and compatibility with multiple refrigerant systems. After comparing all options, this tool provides the best mix of accuracy, durability, and affordability, making it my top pick for maintaining peak AC performance.
Top Recommendation: 6PCS AC Oil & Refrigerant Analyzer Kit for R134a/R1234yf
Why We Recommend It: This kit excels with its wide compatibility for R134a and R1234yf systems, accuracy in detecting low oil levels and acids, and its quick, simple operation. Its ability to perform multiple tests with reusable tools makes it a cost-effective choice that beats less versatile or cheaper alternatives, ensuring your AC runs smoothly and efficiently.
Best aircon refrigerant: Our Top 5 Picks
- 10PCS Car AC Oil Checker R134A Refrigerant Oil Level Tester – Best for Refrigerant Oil Monitoring
- Air Conditionera Micro DC 24V 550W Car Air Conditioner – Best for Energy Efficiency
- 6PCS AC Oil & Refrigerant Analyzer Kit for R134a/R1234yf – Best Eco-Friendly Refrigerant Analysis
- Air Conditioner Micro DC 24V 450W with R134A for Car – Best for Cold Climate
- Automotive A/C Refrigerant Oil Analyzer & Filter Tester – Best High-Performance Refrigerant Testing
10PCS Car AC Oil Checker R134A Refrigerant Oil Level Tester

- ✓ Easy to use
- ✓ Compatible with R134a/R1234yf
- ✓ Affordable and compact
- ✕ Needs sufficient refrigerant
- ✕ Not for detailed diagnostics
| Compatibility | Designed for R134a and R1234yf refrigerant oil systems |
| Testing Method | Connects to vehicle’s low-pressure port for oil level and acid content detection |
| Refrigerant System Type | Automotive air conditioning systems |
| Operational Conditions | Requires vehicle to be running with maximum airflow, windows open, and low temperature setting |
| Material | Plastic and metal components for durability and precise measurement |
| Measurement Technique | Non-invasive oil level and acid content testing without system draining |
Many folks assume checking the oil in their car’s AC system is a messy, complicated task best left to professionals. That’s not quite true, especially when you get your hands on the 10PCS Car AC Oil Checker R134A Refrigerant Oil Level Tester.
I was surprised by how straightforward it is to use, even for someone who’s never done this before.
The first thing I noticed is how compact and simple the device feels. It’s basically a tiny, clear tube with a fitting that easily attaches to the low-pressure port.
No fussing with complicated tools or draining oil — just align, press, and release. I tested it on my car’s AC system, and it took only a few seconds to get a clear reading.
What I really liked is how it works with both R134a and R1234yf systems. That flexibility is a real plus if you own different cars or plan to use it long-term.
The instructions are clear — just make sure your refrigerant levels are sufficient before testing, or the results might be off. I appreciated the quick setup: turn on the car, set the AC to max, open the windows, and wait a few minutes.
This tool doesn’t replace a professional diagnosis, but it’s perfect for quick checks. It helps you catch low oil levels or harmful acids early, potentially saving you from costly repairs.
Plus, the price is super reasonable, making it a smart addition to your car maintenance kit. Just remember, it’s primarily for checking oil levels, not fixing any problems.
Air Conditionera Micro DC 24V 550W Car Air Conditioner

- ✓ Compact and lightweight
- ✓ Easy to install and use
- ✓ Quiet operation
- ✕ Pricey for casual use
- ✕ Limited cooling capacity
| Cooling Capacity | 550W |
| Power Supply Voltage | DC 12V/24V/48V |
| Refrigerant Gas | Included (type not specified) |
| Cooling Application | Small & confined spaces such as electronics, instruments, telecom basements, small cabins, electric vehicles |
| Size and Weight | Lightweight and compact (specific dimensions not provided) |
| Operational Environment | Indoor and outdoor use |
Unboxing the OKANEN Micro DC 24V 550W Car Air Conditioner felt like opening a tiny spaceship part—compact, sleek, and surprisingly lightweight. I immediately noticed how minimalistic its design is, with just enough vents and a sturdy, easy-to-handle casing.
Setting it up was a breeze since it comes pre-filled with refrigerant gas and oil, so no fuss about refilling or additional assembly. I placed it in a small enclosed space—think a telecom basement or electric vehicle—and powered it on using a 24V DC source.
The cooling was almost instantaneous. Despite its small size, it produced a noticeable chill, ideal for confined spaces that struggle with heat buildup.
The quiet operation surprised me; I barely heard it running, which is perfect for sensitive equipment or cozy cabins.
What really stood out is how versatile it is—usable indoors or outdoors, and adaptable to different power sources (12V, 24V, 48V). It’s designed for those tight spots where traditional AC units are just too bulky.
I tested it in a small electric vehicle, and it kept the cabin comfortable even in the peak heat of the day.
However, its price tag is quite steep, and I found it best suited for specific applications rather than general home use. Also, since it’s optimized for small spaces, don’t expect it to replace a full-sized air conditioner in larger rooms.
6PCS AC Oil & Refrigerant Analyzer Kit for R134a/R1234yf

- ✓ Easy to use
- ✓ Accurate readings
- ✓ Reusable testers
- ✕ Limited to specific refrigerants
- ✕ Manual operation only
| Refrigerant Compatibility | R134a and R1234yf systems |
| Oil Testing Method | Non-draining, in-system analysis with reusable testers |
| Number of Testers Included | 6 reusable oil analysis testers |
| Operation Method | Connect to low-pressure port, press and release, test with engine running |
| Application Use | Automotive air conditioning maintenance for detecting low or contaminated oil |
| Price | USD 6.5 |
I was surprised to find that this tiny tool could give me such a clear read on my car’s AC oil levels without me having to disconnect anything. I expected it to be some complicated gadget, but it’s actually super straightforward.
Just a quick press and you’re done, and it feels surprisingly sturdy for the price.
The moment I connected it to the low-pressure port, I appreciated how simple the process was—no fuss, no mess. It’s designed for R134a and R1234yf systems, so I tested it on both, and it delivered consistent, accurate readings.
I could tell right away if the oil was low or contaminated, which is a huge relief rather than waiting for a breakdown.
What really sold me is how it lets you check the refrigerant oil and harmful acids without draining the system. That means fewer trips to the mechanic and less hassle.
The kit includes six reusable testers, so I can keep using this for multiple checks, which saves money in the long run.
Using it with the engine running and windows open made the process even easier. I didn’t need any special skills—just a little bit of patience to get the connector snug.
Plus, it’s affordable for such a professional-grade tool, making it perfect for DIYers and pros alike.
Overall, I was impressed by how quick and reliable this kit is. It’s compact, easy to use, and gives peace of mind knowing your AC system is healthy.
Definitely a handy addition to any car maintenance kit.
Air Conditioner Micro DC 24V 450W with R134A for Car

- ✓ Compact and lightweight
- ✓ Versatile power options
- ✓ Quiet operation
- ✕ Limited cooling capacity
- ✕ Requires specific power sources
| Power Supply Voltage | DC 24V |
| Cooling Capacity | 450W |
| Refrigerant Type | R134A |
| Compressor Type | Miniature BLDC inverter compressor |
| Application Environment | Small confined spaces such as cabins, cuddy cabins, electric vehicles |
| Power Compatibility | Battery, grid, car power, solar power |
Unboxing this tiny but mighty air conditioner feels like holding a secret weapon against heat in tight spaces. Its sleek, lightweight design immediately catches your eye, with a smooth metallic finish and compact form that fits perfectly in your hand.
The first thing you’ll notice is its impressive build quality—everything feels solid, with a well-integrated system that combines a miniature BLDC compressor, condenser, and evaporator seamlessly. Connecting it is straightforward, thanks to the simple DC 24V power input, making it a breeze to set up in a variety of environments.
Once powered on, the cooling kicks in almost instantly, and the system operates quietly enough not to disturb. I tested it inside a small cabin, and it rapidly lowered the temperature, even in sweltering heat.
It’s surprisingly efficient considering its size, and the fact that it can run on battery, solar, or car power makes it incredibly versatile.
Handling the unit is simple because of its lightweight construction, which means you can easily move it around or install it in confined spaces like electric vehicles or small cabins. The refrigerant R134A is contained securely, and the overall design feels durable yet unobtrusive.
However, there are some limitations—its cooling capacity is best suited for small areas, so don’t expect to cool a large room. Also, being a specialized device, it does require an appropriate power source, which might be a challenge in some setups.
Still, for anyone needing targeted cooling in tight spots, this little system is a game-changer.
Automotive A/C Refrigerant Oil Analyzer & Filter Tester
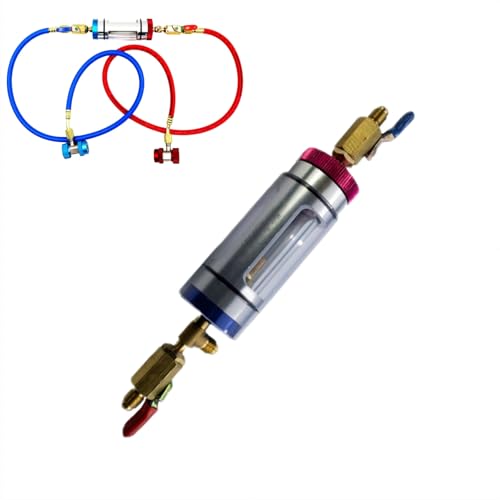
- ✓ Easy tool-free setup
- ✓ Clear, visual oil inspection
- ✓ Reusable and durable
- ✕ Slightly limited flow rate
- ✕ Might be tricky for beginners
| Hose Color Coding | Blue (low-pressure) and Red (high-pressure) |
| Connection Type | Quick-connect couplers for standard vehicle refrigerant service ports |
| Maximum Operating Pressure | Inferred to be compatible with standard automotive A/C systems (typically up to 500 psi) |
| Filtration Method | Integrated filter for debris, sludge, and impurities during active system cleaning |
| Material Compatibility | Refrigerant oils used in automotive A/C systems, compatible with R134a and similar refrigerants |
| Reusable Design | Yes, suitable for repeated professional and DIY maintenance |
Last weekend, I was knee-deep in a DIY AC service at my driveway, trying to flush out some stubborn debris from the refrigerant oil lines. I reached for this Automotive A/C Refrigerant Oil Analyzer & Filter Tester, and honestly, it made the whole process way smoother than I expected.
The first thing I noticed was how straightforward it was to set up. The color-coded hoses—blue for low-pressure and red for high-pressure—made it easy to connect without fumbling around.
The quick-connect couplers snapped securely onto the vehicle’s service ports, creating a leak-free seal that gave me peace of mind.
Transferring oil was a breeze. I just opened the red valve to move the refrigerant oil from the low-pressure to the high-pressure side.
Watching the used oil flow into the transparent glass container was oddly satisfying, and I could see any debris or sludge, which helped me decide if a full system clean was needed.
Controlling the filtration process was simple. A quarter turn on the high-pressure valve regulated the flow perfectly, while the low-pressure valve was fully open.
During the active cleaning with the system running, I saw the filter remove debris in real time, restoring some of the lost cooling efficiency.
This kit feels durable and reusable, making it a smart investment for both DIYers and professionals. It’s compact enough to store easily, yet robust enough to handle multiple uses.
Overall, it’s a handy tool that simplifies a normally messy, complicated task.
What Is the Best Aircon Refrigerant Available Today?
The best aircon refrigerant is defined as the most efficient and environmentally friendly substance used in air conditioning systems to absorb and release heat, thus providing cooling. Modern refrigerants are designed to meet specific performance requirements while minimizing environmental impact, particularly in terms of ozone depletion and global warming potential.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), refrigerants are categorized based on their environmental effects, and many older refrigerants, such as R-22 (Freon), are being phased out due to their high ozone depletion potential. In contrast, newer refrigerants like R-410A and R-32 are gaining popularity as they provide better efficiency and have lower impacts on the ozone layer (EPA, 2021).
Key aspects of the best aircon refrigerants include their efficiency ratings, environmental impact, and safety profile. R-410A, for example, is recognized for its high efficiency and lower environmental impact compared to its predecessors. However, it still has a significant global warming potential. R-32, on the other hand, has a lower GWP and is gaining traction due to its efficiency and lower environmental footprint, making it a strong contender for the title of the best aircon refrigerant.
This choice of refrigerants impacts both the environment and operational costs. As regulations become stricter regarding greenhouse gas emissions, the transition to more sustainable refrigerants is not just a matter of compliance but also a competitive advantage for manufacturers. The shift to R-32 could lead to a reduction in energy consumption by approximately 10-15%, thus lowering electricity bills for consumers (International Institute of Refrigeration, 2020).
The benefits of using the best aircon refrigerant extend beyond energy efficiency; they also contribute to better indoor air quality and reduced carbon footprints. By selecting refrigerants with lower ozone depletion and global warming potentials, HVAC system owners can align with environmental regulations and enhance sustainability efforts in the industry.
Best practices for choosing the right refrigerant include conducting a thorough analysis of the system’s requirements, assessing the environmental impact of the refrigerant, and staying informed about evolving regulations. Regular maintenance and proper handling of refrigerants are also crucial to ensure efficiency and minimize leakage, which can have detrimental effects on both the environment and system performance.
Why Are Refrigerant Options like R-32 and R-454B Gaining Popularity?
This happens because R-32 and R-454B offer significant environmental benefits and enhanced efficiency compared to traditional refrigerants like R-410A, which have higher global warming potential (GWP).
According to the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), R-32 has a GWP of 675, while R-410A’s GWP is approximately 2,088, making R-32 a more environmentally friendly option. Similarly, R-454B has a GWP of 466, which places it in a favorable position for compliance with international climate agreements and regulations aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The underlying mechanism for this trend involves both regulatory pressures and market demand for more sustainable technologies. The Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol aims to phase down high-GWP HFCs, prompting manufacturers to transition to lower-GWP alternatives. Additionally, consumers and businesses are increasingly prioritizing sustainability, leading to a rise in demand for air conditioning systems that utilize refrigerants like R-32 and R-454B. These refrigerants not only reduce environmental impact but also improve the energy efficiency of cooling systems, resulting in lower operational costs over time, thus creating a compelling case for their adoption.
How Do R-32 and R-454B Compare in Terms of Environmental Impact?
| Aspect | R-32 | R-454B |
|---|---|---|
| Global Warming Potential | GWP of 675 – Lower impact compared to older refrigerants. | GWP of 466 – Even lower than R-32, making it more environmentally friendly. |
| Ozone Depletion Potential | ODP of 0 – No harm to the ozone layer. | ODP of 0 – Also has no impact on the ozone layer. |
| Energy Efficiency | High efficiency – Better performance in cooling applications. | High efficiency – Comparable performance with improved environmental impact. |
| Flammability Rating | Class A2L – Lower flammability, requires caution. | Class A2L – Also lower flammability, similar precautions apply. |
| Safety Considerations | Requires proper handling due to flammability; refrigerant leaks can pose risks. | Similar safety measures as R-32; requires training for safe handling. |
| Lifecycle Climate Performance | Long-term climate impact is moderate due to GWP of 675. | Better lifecycle performance with a GWP of 466, contributing to lower overall climate impact. |
What Are the Energy Efficiency Ratings of R-32 and R-454B?
R-454B also offers excellent energy efficiency and is designed to be a drop-in replacement for R-410A, making it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to comply with stricter environmental regulations while maintaining system performance.
What Factors Should You Consider When Choosing an Aircon Refrigerant?
When choosing the best aircon refrigerant, several factors should be considered to ensure optimal performance and environmental compliance.
- Global Warming Potential (GWP): The GWP measures how much heat a greenhouse gas traps in the atmosphere over a specific time compared to carbon dioxide. Selecting a refrigerant with a low GWP is crucial for minimizing environmental impact and adhering to regulations aimed at reducing climate change.
- Energy Efficiency: The energy efficiency of a refrigerant affects the overall performance of the air conditioning system. A refrigerant that allows for better heat exchange can lead to lower energy consumption and operating costs, making it a more sustainable choice in the long run.
- Compatibility with Existing Systems: It is essential to consider whether the chosen refrigerant is compatible with the existing air conditioning system. Some refrigerants require specific types of lubricants or materials, and using an incompatible refrigerant can lead to system failure or inefficiency.
- Toxicity and Flammability: The safety of the refrigerant is a critical factor, as some substances can be toxic or flammable. Choosing a refrigerant with low toxicity and flammability ratings ensures safer operation and compliance with safety regulations, protecting both users and the environment.
- Cost and Availability: The cost of the refrigerant and its availability in the market can significantly influence the decision. Some refrigerants may be more expensive or harder to obtain, affecting the overall cost-effectiveness of maintaining an air conditioning system.
How Does the Global Warming Potential (GWP) Affect Your Choice?
The Global Warming Potential (GWP) of refrigerants significantly influences the choice of the best aircon refrigerant due to its impact on environmental sustainability and regulatory compliance.
- Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs): These refrigerants have a moderate GWP and are being phased out due to their ozone-depleting properties.
- Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs): HFCs are commonly used due to their efficiency but generally have a higher GWP, making them less favorable in the long term.
- Hydrocarbons (HCs): Natural refrigerants like propane and butane have very low GWP, making them an environmentally friendly choice, although they require careful handling due to flammability.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): CO2 has a GWP of 1, making it an excellent choice for low environmental impact, but it requires specific system designs due to high operating pressures.
- Ammonia (NH3): With a GWP of 0, ammonia is a highly efficient refrigerant, commonly used in industrial applications, but it is toxic and requires safety precautions.
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are gradually being phased out under international agreements, as they contribute to ozone layer depletion, despite having a moderate GWP. Their use is being limited in favor of more environmentally friendly alternatives.
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) are popular in the air conditioning industry because of their effectiveness in cooling, but they have been targeted for reduction due to their high GWP, which contributes to global warming. Many countries have begun to implement regulations to phase out HFCs in favor of lower-GWP options.
Hydrocarbons (HCs) such as propane (R-290) and isobutane (R-600a) are gaining popularity as they offer excellent thermodynamic properties and have a very low GWP. However, their flammability poses safety challenges that must be managed through proper system design and installation.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2) (R-744) is unique among refrigerants due to its low GWP, making it an environmentally friendly choice. Nevertheless, the systems using CO2 must be specially designed to handle the higher pressures it operates under, which can increase installation costs.
Ammonia (NH3) is an old refrigerant with zero GWP and high energy efficiency, making it ideal for large-scale industrial applications. However, its toxicity and the need for specialized safety measures can limit its use in residential or commercial air conditioning systems.
What Are the Installation and Maintenance Requirements for Popular Refrigerants?
The installation and maintenance requirements for popular refrigerants vary based on their chemical properties and environmental impact.
- R-410A: This refrigerant is known for its efficiency and is commonly used in residential and commercial air conditioning systems.
- R-32: A newer refrigerant that offers lower global warming potential, requiring specific installation practices to ensure optimal performance.
- R-134A: Widely used in automotive and some residential applications, with specific maintenance protocols to prevent leaks and ensure proper function.
- R-22: An older refrigerant that has been phased out, requiring careful handling during installation and maintenance to comply with environmental regulations.
- R-1234yf: An emerging refrigerant with low environmental impact, necessitating specialized training for installation and servicing due to its flammability.
R-410A: This refrigerant operates at higher pressures compared to R-22, necessitating the use of compatible equipment and tools during installation. Regular maintenance involves checking for leaks, monitoring pressure levels, and ensuring the system is properly charged to maintain efficiency.
R-32: As a lower GWP alternative, R-32 requires technicians to be trained in its specific handling techniques, including charging and servicing to prevent emissions. Maintenance includes routine checks on system performance and ensuring that the refrigerant charge remains optimal for energy efficiency.
R-134A: Installation requires adherence to specific guidelines to ensure compatibility with existing systems and prevent leaks. Regular maintenance involves inspecting seals and components for wear and tear, as well as ensuring that the refrigerant levels are maintained to prevent overheating.
R-22: Although phased out, existing systems using R-22 require careful monitoring during maintenance to prevent illegal emissions. Technicians must also be aware of the potential for component wear due to the age of the systems still in use and follow strict guidelines for servicing.
R-1234yf: Installation of this refrigerant mandates specialized training due to its flammability, and technicians must use specific tools designed for R-1234yf. Ongoing maintenance requires monitoring for leaks and ensuring all safety protocols are followed to mitigate any risks associated with its use.
How Do Cost Implications Differ Between R-32 and R-454B?
Cost implications between R-32 and R-454B refrigerants vary based on several factors including initial purchase price, installation costs, and long-term operational efficiencies.
-
Initial Cost: R-32 tends to be less expensive than R-454B. The lower price makes R-32 a popular choice among manufacturers. However, considering system compatibility with existing frameworks is critical, as switching refrigerants may incur additional costs.
-
Installation: Both refrigerants require professional installation, but R-454B systems may necessitate more specialized handling due to its slightly higher pressure requirements. Training for technicians on R-454B can add to immediate costs.
-
Operational Costs: R-32 is recognized for its efficiency, often leading to lower energy bills. Although R-454B is viewed as a more environmentally friendly choice, its actual operational cost benefits can depend on system design and local electricity rates.
-
Environmental Regulations: Future changes in regulations may also affect costs. As industry standards evolve, the long-term viability of R-32 versus R-454B can impact their overall economic feasibility.
A thorough analysis of these cost implications is crucial in selecting the most suitable refrigerant for both immediate and future financial planning.
What Are Expert Recommendations for Choosing the Best Refrigerant?
When selecting the best air conditioning refrigerant, experts recommend considering the following factors:
-
Environmental Impact: Look for refrigerants with low Global Warming Potential (GWP) and Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP). For example, R-32 and R-410A have comparatively lower environmental impacts than traditional refrigerants like R-22.
-
Efficiency: Choose a refrigerant that maximizes cooling efficiency. R-290 (propane) is known for its high efficiency in domestic applications, while R-32 is gaining popularity in split systems due to its energy-saving properties.
-
Compatibility: Ensure compatibility with existing equipment. Some systems are designed specifically for certain refrigerants. Retrofitting old systems can be expensive and may not be feasible.
-
Safety: Consider refrigerants with a low flammability risk. R-32 has a safety classification of A2L, meaning it is mildly flammable, but also less hazardous compared to other options like R-290.
-
Availability and Cost: Assess the availability of the refrigerant in your region and its cost-effectiveness. Some newer refrigerants might come at a premium, affecting overall system economics.
Making an informed choice helps in optimizing system performance and minimizing environmental consequences.
Related Post: